Climate change stands as one of the most pressing challenges of our time, influencing every corner of the globe and demanding immediate action. It refers to long-term shifts in climate patterns, particularly an alarming rise in global temperatures. While natural processes have always played a role in altering the Earth's climate, human activities have accelerated these changes at an unprecedented rate, leading to what we now call anthropogenic climate change.
In this post, we’ll explore the causes, impacts, and potential solutions for addressing this global crisis.
What is Climate Change?
Climate change encompasses significant and enduring changes in the Earth's climate system. Historically, the planet's climate has evolved due to factors like volcanic eruptions, shifts in Earth's orbit, and solar radiation. However, over the past century, human-induced factors—primarily greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions—have dramatically increased the pace and intensity of these changes.
The Science Behind It
GHGs like carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O) are major contributors to the greenhouse effect, a process where these gases trap heat in the atmosphere, causing global warming. Key sources of these emissions include:
- Burning fossil fuels for energy.
- Deforestation and land-use changes.
- Industrial processes and agriculture.
The result? Rising global temperatures, disrupted ecosystems, and severe socio-economic impacts.
Impacts of Climate Change
1. Rising Temperatures and Global Warming
The Earth's average surface temperature has already increased by approximately 1.2°C since pre-industrial times. If current trends continue, this rise could reach 4°C by the end of the century.
Challenges:
- Heatwaves: Increased temperatures lead to heat-related illnesses, wildfires, and disruptions to agriculture.
- Polar Ice Melt: Accelerated ice loss in polar regions contributes to sea-level rise.
- Health Impacts: Warming exacerbates respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and the spread of vector-borne diseases like malaria.
_0.png) |
| Annual global mean temperature anomalies from January – September 2024 (relative to the 1850-1900 average) from six international datasets. |
2. Extreme Weather Events
Climate change has intensified extreme weather events, including hurricanes, floods, droughts, and wildfires.
Challenges:
- Flooding: Heavier rainfall leads to more frequent and severe floods, causing significant economic and social losses.
- Drought: Prolonged droughts disrupt water supply, agriculture, and ecosystems.
- Wildfires: Regions like California and Australia face longer fire seasons with devastating impacts on communities and biodiversity.
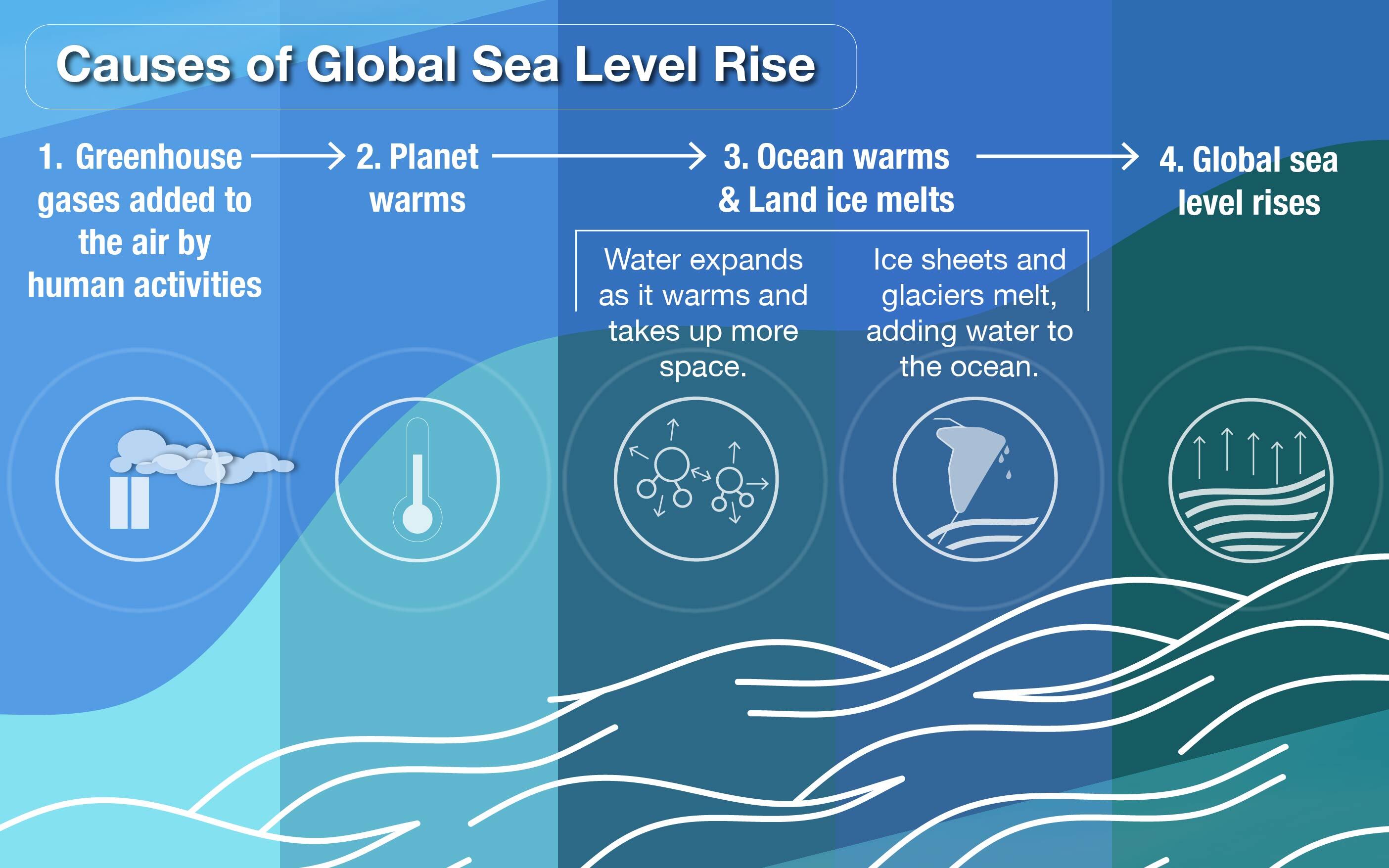
3. Sea-Level Rise
Melting glaciers and the thermal expansion of seawater are causing sea levels to rise, threatening coastal cities and ecosystems.
Challenges:
- Coastal erosion and flooding endanger cities like New York, Miami, and Dhaka.
- Displacement of coastal populations creates climate refugees.
- Marine ecosystems, including coral reefs and mangroves, face destruction.
4. Loss of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Disruption
As temperatures rise, ecosystems are struggling to adapt. Species are migrating, habitats are disappearing, and the balance of biodiversity is at risk.
Challenges:
- Extinctions of species unable to adapt to rapid changes.
- Ocean acidification from CO₂ absorption affects marine life, including coral reefs and shellfish.
- Shifting habitats disrupt ecosystems and human activities.
5. Social and Economic Impacts
The ripple effects of climate change extend far beyond the environment.
Challenges:
- Poverty and Inequality: Vulnerable communities in developing nations face disproportionate impacts.
- Food Security: Unpredictable weather disrupts agriculture, threatening global food supply chains.
- Economic Losses: Infrastructure damage and adaptation costs strain economies worldwide.
Solutions: Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing climate change requires a dual approach: mitigation (reducing GHG emissions) and adaptation (adjusting to climate impacts).
Mitigation Strategies
- Transition to renewable energy sources like solar and wind.
- Invest in carbon capture and storage technologies.
- Protect and restore natural carbon sinks, such as forests and wetlands.
Adaptation Strategies
- Design resilient infrastructure to withstand extreme weather.
- Implement efficient water management policies.
- Engage local communities in adaptation planning tailored to their needs.
The Role of Global Cooperation
Climate change is a global issue that requires collective action. Agreements like the Paris Agreement aim to limit global warming to below 2°C, with an aspirational target of 1.5°C. However, political and economic challenges often hinder progress.
Key priorities include:
- Strengthening international cooperation.
- Integrating climate considerations into national policies.
- Ensuring climate justice for marginalized and vulnerable populations.
A Call to Action
Climate change is one of humanity's greatest challenges, but it also presents an opportunity for innovation and collaboration. By prioritizing sustainability, embracing clean energy, and fostering global solidarity, we can pave the way for a future that safeguards our planet for generations to come.
The time to act is now. Together, we can make a difference.







-800x447.png)




What do you think? Please let me know.